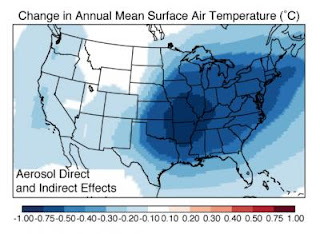
Climate scientists at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have discovered that particulate pollution in the late 20th century created a "warming hole" over the eastern United States—that is, a cold patch where the effects of global warming were temporarily obscured.
While greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane warm the Earth's surface, tiny particles in the air can have the reverse effect on regional scales.
"What we've shown is that particulate pollution over the eastern United States has delayed the warming that we would expect to see from increasing greenhouse gases," says lead author Eric Leibensperger (Ph.D. '11), who completed the work as a graduate student in applied physics at SEAS.
"For the sake of protecting human health and reducing acid rain, we've now cut the emissions that lead to particulate pollution," he adds, "but these cuts have caused the greenhouse warming in this region to ramp up to match the global trend."
At this point, most of the "catch-up" warming has already occurred.
The findings, published in the journal Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, present a more complete picture of the processes that affect regional climate change. The work also carries significant implications for the future climate of industrial nations, like China, that have not yet implemented air quality regulations to the same extent as the United States.
Until the United States passed the Clean Air Act in 1970 and strengthened it in 1990, particulate pollution hung thick over the central and eastern states. Most of these particles in the atmosphere were made of sulfate, originating as sulfur emissions from coal-fired power plants. Compared to greenhouse gases, particulate pollution has a very short lifetime (about 1 week), so its distribution over the Earth is uneven.
"The primary driver of the warming hole is the aerosol pollution—these small particles," says Leibensperger. "What they do is reflect incoming sunlight, so we see a cooling effect at the surface."
This effect has been known for some time, but the new analysis demonstrates the strong impact that decreases in particulate pollution can have on regional climate.
The researchers found that interactions between clouds and particles amplified the cooling. Particles of pollution can act as nucleation sites for cloud droplets, which can in turn reflect even more sunlight than the particles would individually, leading to greater cooling at the surface.
This was something I brought up back in 2005 when I as working with the climate guys here. Pollution and particulates make a big difference.
Link.

No comments:
Post a Comment